PLASMA REMEDIATION OF GREENHOUSE GASES IN SEMICONDUCTOR PROCESSING
Xudong "Peter" Xu and Mark J. Kushner
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING
University of Illinois at Urbana/Champaign
Semiconductor microelectronics fabrication uses plasma processing for etching and deposition. These processes use gases which have large global warming potentials. In etching and chamber cleaning, Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs), typically including CF4, C2F6, CHF3, NF3, SF6 and C3F8, are used to generate reactive F atoms. Due to underutilization of the feedstock gases or secondary production of species, the effluent from the reactor contains many of these gases. A plasma remediation method for abating PFC emissions is presented.
Methodology
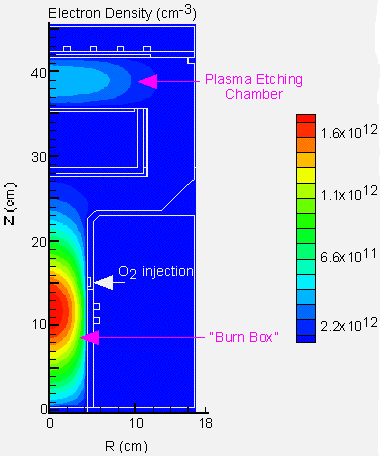
We have used the Hybrid Plasma Equipment Model to simulate the dissociation of feedstock greenouse gases in an inductively coupled plasma reactor, and their subsequent remediation in a downstream "burn-box".
Results:
We consider Ar/CF4 as the process gas mixture with O2 injected downstream to facilitate oxidation of the undissociated CF4, gas phase reaction products (e.g., C2F6, C2F4) and etch product (SiF4). The electron density is shown for a combined plasma etching chamber and downstream burn-box.